Creating Content#
Jupyter Book allows for the integration of various markup languages and formats, including Markdown files, Jupyter notebooks, MyST Markdown notebooks, reStructured Text and more.
MyST is a markup language that draws inspiration from RMarkdown, and is fully integrated for the use with Jupyter Book. It allows for more advanced formatting options and the ability to include interactive elements, such as widgets and code snippets, within your content. Jupyter Book is able to parse MyST in both .ipybn and .md files, allowing for flexible content creation.
Here, we present only a short overview of the features of MyST, however, there is much more documentation on the MyST website.
Before we get started…#
most of what you’ll see within this lecture was prepared by Ross Markello, Michael Notter and Peer Herholz and further adapted for this course by Michael Ernst and Felix Körber
based on Tal Yarkoni’s “Introduction to Python” lecture at Neurohackademy 2019
based on http://www.stavros.io/tutorials/python/ & http://www.swaroopch.com/notes/python
based on oesteban/biss2016 & jvns/pandas-cookbook
Objectives 📍#
learn basic and efficient usage of the
jupyter ecosystem¬ebookswhat is
Jupyter& how to utilizejupyter notebooks
First things first#
Open up Visual Studio Code (or Jupyter Lab if you prefer using that). Create a new file, by clicking on “File” and then on “New File”. Here, you can choose which file format you want to choose. Choose .iypbn for interactive Files or create a new .md (Markdown) file in the folder for your project.
To Jupyter & beyond#

a community of people
an ecosystem of open tools and standards for interactive computing
language-agnostic and modular
empower people to use other open tools
To Jupyter & beyond#

We’re going to be working in Jupyter notebooks for most of this presentation! However, Visual Studio Code is not too different.
Files Tab#
The files tab provides an interactive view of the portion of the filesystem which is accessible by the user. This is typically rooted by the directory in which the notebook server was started.
The top of the files list displays clickable breadcrumbs of the current directory. It is possible to navigate the filesystem by clicking on these breadcrumbs or on the directories displayed in the notebook list.
A new notebook can be created by clicking on the New dropdown button at the top of the list, and selecting the desired language kernel.
Notebooks can also be uploaded to the current directory by dragging a notebook file onto the list or by clicking the Upload button at the top of the list.
The Notebook#
When a notebook is opened, a new browser tab will be created which presents the notebook user interface (UI). This UI allows for interactively editing and running the notebook document.
A new notebook can be created from the dashboard by clicking on the Files tab, followed by the New dropdown button, and then selecting the language of choice for the notebook.
An interactive tour of the notebook UI can be started by selecting Help -> User Interface Tour from the notebook menu bar.
Header#
At the top of the notebook document is a header which contains the notebook title, a menubar, and toolbar. This header remains fixed at the top of the screen, even as the body of the notebook is scrolled. The title can be edited in-place (which renames the notebook file), and the menubar and toolbar contain a variety of actions which control notebook navigation and document structure.
Body#
The body of a notebook is composed of cells. Each cell contains either markdown, code input, code output, or raw text. Cells can be included in any order and edited at-will, allowing for a large amount of flexibility for constructing a narrative.
Markdown cells- These are used to build anicely formatted narrativearound thecodein the document. The majority of this lesson is composed ofmarkdown cells.to get a
markdown cellyou can either select thecelland useesc+mor viaCell -> cell type -> markdown
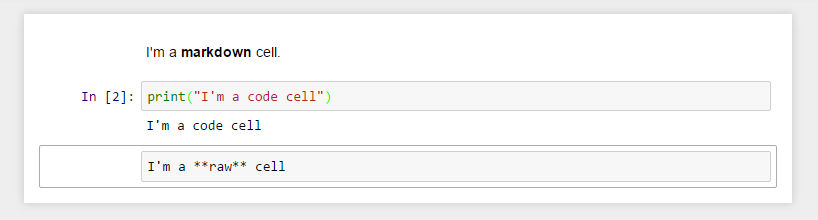
Code cells- These are used to define thecomputational codein thedocument. They come intwo forms:the
input cellwhere theusertypes thecodeto beexecuted,and the
output cellwhich is therepresentationof theexecuted code. Depending on thecode, thisrepresentationmay be asimple scalar value, or something more complex like aplotor aninteractive widget.
to get a
code cellyou can either select thecelland useesc+yor viaCell -> cell type -> code

Raw cells- These are used whentextneeds to be included inraw form, withoutexecutionortransformation.

Modality#
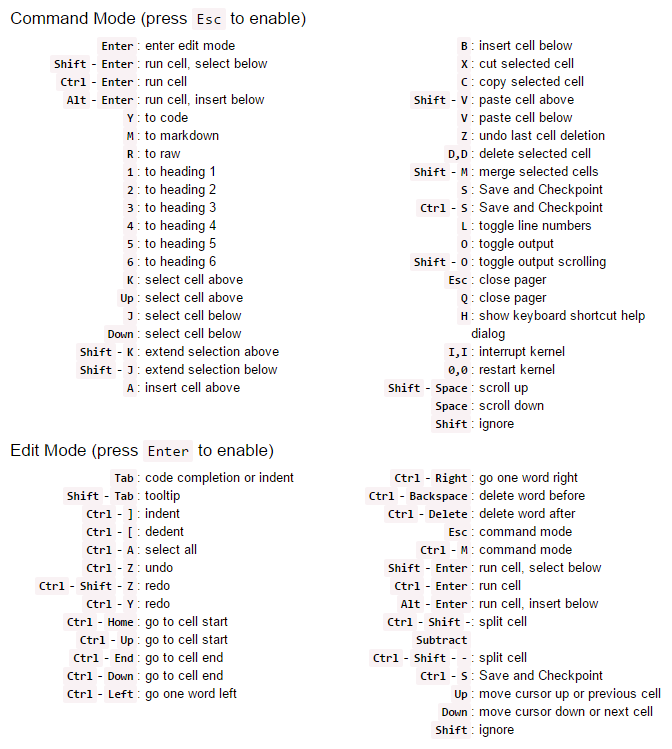
The notebook user interface is modal. This means that the keyboard behaves differently depending upon the current mode of the notebook. A notebook has two modes: edit and command.
Edit mode is indicated by a green cell border and a prompt showing in the editor area. When a cell is in edit mode, you can type into the cell, like a normal text editor.

Command mode is indicated by a grey cell border. When in command mode, the structure of the notebook can be modified as a whole, but the text in individual cells cannot be changed. Most importantly, the keyboard is mapped to a set of shortcuts for efficiently performing notebook and cell actions. For example, pressing c when in command mode, will copy the current cell; no modifier is needed.

Tab Completion#
One of the most useful things about Jupyter Notebook is its tab completion.
Try this: click just after read_csv( in the cell below and press Shift+Tab 4 times, slowly. Note that if you’re using JupyterLab you don’t have an additional help box option.
pd.read_csv(
After the first time, you should see this:
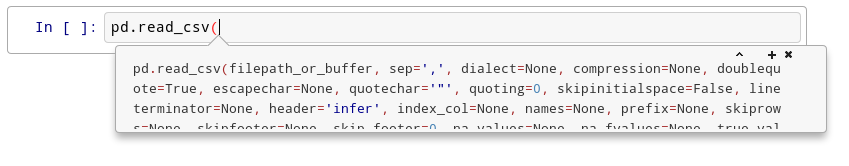
After the second time:
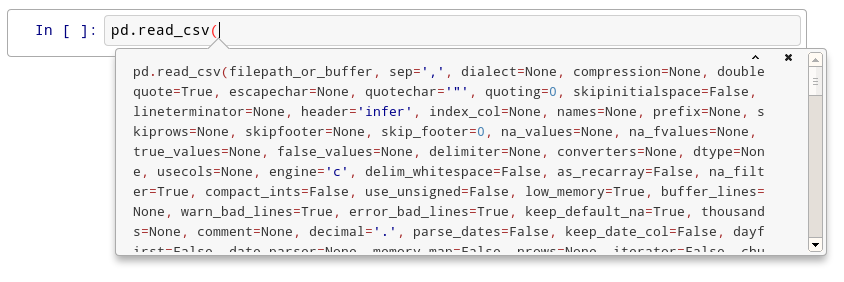
After the fourth time, a big help box should pop up at the bottom of the screen, with the full documentation for the read_csv function:
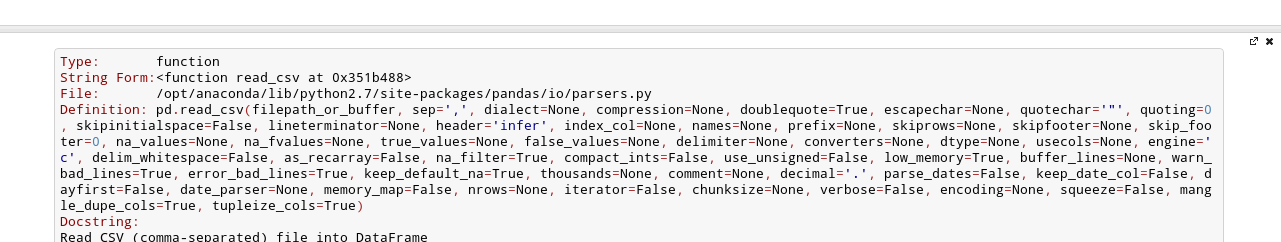
This is amazingly useful. You can think of this as “the more confused I am, the more times I should press Shift+Tab”.
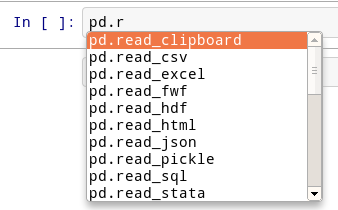
Okay, let’s try tab completion for function names!
pd.r
You should see this:
Get Help#
There’s an additional way on how you can reach the help box shown above after the fourth Shift+Tab press. Instead, you can also use obj? or obj?? to get help or more help for an object.
pd.read_csv?
Writing code#
Writing code in a notebook is pretty normal.
def print_10_nums():
for i in range(10):
print(i)
print_10_nums()
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
If you messed something up and want to revert to an older version of a code in a cell, use Ctrl+Z or to go than back Ctrl+Y.
For a full list of all keyboard shortcuts, click on the small keyboard icon in the notebook header or click on Help > Keyboard Shortcuts.
The interactive workflow: input, output, history#
Notebooks provide various options for inputs and outputs, while also allowing to access the history of run commands.
2+10
12
_+10
22
You can suppress the storage and rendering of output if you append ; to the last cell (this comes in handy when plotting with matplotlib, for example):
10+20;
_
22
The output is stored in _N and Out[N] variables:
_8 == Out[8]
True
Previous inputs are available, too:
In[9]
'_8 == Out[8]'
_i
'In[9]'
%history -n 1-5
1:
import pandas as pd
print("Hi! This is a cell. Click on it and press the ▶ button above to run it")
2: pd.read_csv?
3:
def print_10_nums():
for i in range(10):
print(i)
4: print_10_nums()
5: 2+10
Accessing the underlying operating system#
Through notebooks you can also access the underlying operating system and communicate with it as you would do in e.g. a terminal via bash:
!pwd
/Users/peerherholz/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction
files = !ls
print("My current directory's files:")
print(files)
My current directory's files:
['fancy_analyzes.py', 'gui_cli_example_bash.sh', 'gui_cli_example_python.py', 'intro_jupyter.ipynb', 'intro_to_git_and_github.ipynb', 'intro_to_shell.ipynb', 'introduction.md', 'introduction_1.md', 'introduction_2.md', 'introduction_3.md']
!echo $files
[fancy_analyzes.py, gui_cli_example_bash.sh, gui_cli_example_python.py, intro_jupyter.ipynb, intro_to_git_and_github.ipynb, intro_to_shell.ipynb, introduction.md, introduction_1.md, introduction_2.md, introduction_3.md]
!echo {files[0].upper()}
FANCY_ANALYZES.PY
Magic functions#
IPython has all kinds of magic functions. Magic functions are prefixed by % or %%, and typically take their arguments without parentheses, quotes or even commas for convenience. Line magics take a single % and cell magics are prefixed with two %%.
%magic
Line vs cell magics:
%timeit list(range(1000))
11.6 µs ± 247 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
%%timeit
list(range(10))
list(range(100))
1.22 µs ± 9.79 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
Line magics can be used even inside code blocks:
for i in range(1, 5):
size = i*100
print('size:', size, end=' ')
%timeit list(range(size))
size: 100 852 ns ± 23.2 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
size: 200 1.27 µs ± 54.3 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
size: 300 2.05 µs ± 50.4 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
size: 400 3.37 µs ± 42.7 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)
Magics can do anything they want with their input, so it doesn’t have to be valid Python:
%%bash
echo "My shell is:" $SHELL
echo "My disk usage is:"
df -h
My shell is: /bin/bash
My disk usage is:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Capacity iused ifree %iused Mounted on
/dev/disk1s1 466Gi 10Gi 50Gi 18% 488411 4881964469 0% /
devfs 200Ki 200Ki 0Bi 100% 705 0 100% /dev
/dev/disk1s2 466Gi 394Gi 50Gi 89% 4642743 4877810137 0% /System/Volumes/Data
/dev/disk1s5 466Gi 11Gi 50Gi 19% 11 4882452869 0% /private/var/vm
map auto_home 0Bi 0Bi 0Bi 100% 0 0 100% /System/Volumes/Data/home
Another interesting cell magic: create any file you want locally from the notebook:
%%writefile test.txt
This is a test file!
It can contain anything I want...
And more...
Writing test.txt
!cat test.txt
This is a test file!
It can contain anything I want...
And more...
Let’s see what other magics are currently defined in the system:
%lsmagic
Available line magics:
%alias %alias_magic %autoawait %autocall %automagic %autosave %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %conda %config %connect_info %cp %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %pip %popd %pprint %precision %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %qtconsole %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
Available cell magics:
%%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%js %%latex %%markdown %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
Automagic is ON, % prefix IS NOT needed for line magics.
Running normal Python code: execution and errors#
Not only can you input normal Python code, you can even paste straight from a Python or IPython shell session:
>>> # Fibonacci series:
... # the sum of two elements defines the next
... a, b = 0, 1
>>> while b < 10:
... print(b)
... a, b = b, a+b
1
1
2
3
5
8
In [1]: for i in range(10):
print(i, end=' ')
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
And when your code produces errors, you can control how they are displayed with the %xmode magic:
%%writefile mod.py
def f(x):
return 1.0/(x-1)
def g(y):
return f(y+1)
Writing mod.py
Now let’s call the function g with an argument that would produce an error:
import mod
mod.g(0)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-30-81c06c6c0e90> in <module>
1 import mod
----> 2 mod.g(0)
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in g(y)
4
5 def g(y):
----> 6 return f(y+1)
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in f(x)
1
2 def f(x):
----> 3 return 1.0/(x-1)
4
5 def g(y):
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
%xmode plain
mod.g(0)
Exception reporting mode: Plain
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-31-46ce8a1dbba1>", line 2, in <module>
mod.g(0)
File "/Users/peerherholz/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py", line 6, in g
return f(y+1)
File "/Users/peerherholz/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py", line 3, in f
return 1.0/(x-1)
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
%xmode verbose
mod.g(0)
Exception reporting mode: Verbose
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-32-3f57d27a0745> in <module>
1 get_ipython().run_line_magic('xmode', 'verbose')
----> 2 mod.g(0)
global mod.g = <function g at 0x7f81988926a8>
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in g(y=0)
4
5 def g(y):
----> 6 return f(y+1)
global f = <function f at 0x7f819a58b7b8>
y = 0
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in f(x=1)
1
2 def f(x):
----> 3 return 1.0/(x-1)
x = 1
4
5 def g(y):
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
The default %xmode is “context”, which shows additional context but not all local variables. Let’s restore that one for the rest of our session.
%xmode context
Exception reporting mode: Context
Running code in other languages with special %% magics#
%%perl
@months = ("July", "August", "September");
print $months[0];
July
%%ruby
name = "world"
puts "Hello #{name.capitalize}!"
Hello World!
/System/Library/Frameworks/Ruby.framework/Versions/2.6/usr/lib/ruby/2.6.0/universal-darwin19/rbconfig.rb:229: warning: Insecure world writable dir /Users/peerherholz in PATH, mode 040707
Raw Input in the notebook#
Since 1.0 the IPython notebook web application supports raw_input which for example allow us to invoke the %debug magic in the notebook:
mod.g(0)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-36-9fa96bd6b3b6> in <module>
----> 1 mod.g(0)
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in g(y)
4
5 def g(y):
----> 6 return f(y+1)
~/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py in f(x)
1
2 def f(x):
----> 3 return 1.0/(x-1)
4
5 def g(y):
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
%debug
> /Users/peerherholz/google_drive/GitHub/Python_for_Psychologists_Winter2021/lecture/introduction/mod.py(3)f()
1
2 def f(x):
----> 3 return 1.0/(x-1)
4
5 def g(y):
ipdb> exit()
Don’t forget to exit your debugging session. Raw input can of course be used to ask for user input:
enjoy = input('Are you enjoying this tutorial? ')
print('enjoy is:', enjoy)
Are you enjoying this tutorial? only the snacks
enjoy is: only the snacks
The IPython kernel/client model#
%connect_info
{
"shell_port": 60588,
"iopub_port": 60589,
"stdin_port": 60590,
"control_port": 60592,
"hb_port": 60591,
"ip": "127.0.0.1",
"key": "812112ff-f84b0658089eed0149a24418",
"transport": "tcp",
"signature_scheme": "hmac-sha256",
"kernel_name": ""
}
Paste the above JSON into a file, and connect with:
$> jupyter <app> --existing <file>
or, if you are local, you can connect with just:
$> jupyter <app> --existing kernel-55f10c28-d38e-452f-b5fa-6002071b8179.json
or even just:
$> jupyter <app> --existing
if this is the most recent Jupyter kernel you have started.
We can connect automatically a Qt Console to the currently running kernel with the %qtconsole magic, or by typing ipython console --existing <kernel-UUID> in any terminal:
%qtconsole
Saving a Notebook#
Jupyter Notebooks autosave, so you don’t have to worry about losing code too much. At the top of the page you can usually see the current save status:
Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (unsaved changes)
Last Checkpoint: a few seconds ago (autosaved)
If you want to save a notebook on purpose, either click on File > Save and Checkpoint or press Ctrl+S.
To Jupyter & beyond#

Open a terminal
Type
jupyter lab
If you’re not automatically directed to a webpage copy the URL printed in the terminal and paste it in your browser
Click “New” in the top-right corner and select “Python 3”
You have a
Jupyter notebookwithinJupyter lab!